Table Of Content

The new map includes 52 districts, one fewer seat than before due to the state’s relatively flat population growth. Enter your address below or click on the map of current boundaries to see how your district has changed. Until the 1929 stock market crash, most of the dozen women elected to the House were Republicans, and for several decades afterward, the two parties’ numbers were generally close in that chamber.
Reapportionment
House Republicans' Party-Line Majority Hangs by a Thread - Newsweek
House Republicans' Party-Line Majority Hangs by a Thread.
Posted: Wed, 20 Mar 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The Constitution vests certain exclusive powers in the House of Representatives, including the right to initiate impeachment proceedings and to originate revenue bills. The organization and character of the House of Representatives have evolved under the influence of political parties, which provide a means of controlling proceedings and mobilizing the necessary majorities. Party leaders, such as the speaker of the House and the majority and minority leaders, play a central role in the operations of the institution. Also referred to as a congressman or congresswoman, each representative is elected to a two-year term serving the people of a specific congressional district.
Find Your Representative and Senators
A further dominating element of House organization is the committee system, under which the membership is divided into specialized groups for purposes such as holding hearings, preparing bills for the consideration of the entire House, and regulating House procedure. Almost all bills are first referred to a committee, and ordinarily the full House cannot act on a bill until the committee has “reported” it for floor action. There are approximately 20 standing (permanent) committees, organized mainly around major policy areas, each having staffs, budgets, and subcommittees. They may hold hearings on questions of public interest, propose legislation that has not been formally introduced as a bill or resolution, and conduct investigations. Among important standing committees are those on appropriations, on ways and means (which handles matters related to finance), and on rules. There are also select and special committees, which are usually appointed for a specific project and for a limited period.
Table 1. Apportionment Population and Number of Representatives by State: 2020 Census
Puerto Rico also elects a resident commissioner every four years. In most states, major party candidates for each district are nominated in partisan primary elections, typically held in spring to late summer. Exceptions can result in so-called floor fights—convention votes by delegates, with outcomes that can be hard to predict. Especially if a convention is closely divided, a losing candidate may contend further by meeting the conditions for a primary election. The courts generally do not consider ballot access rules for independent and third party candidates to be additional qualifications for holding office and no federal statutes regulate ballot access. As a result, the process to gain ballot access varies greatly from state to state, and in the case of a third party in the United States may be affected by results of previous years' elections.
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
South Carolina
But the gap widened in the 1970s and has persisted, despite a temporary narrowing during the Reagan-Bush 1980s. Brian Frederick, a political scientist at Bridgewater State University, studies apportionment issues and has argued that the House should be expanded. He notes how the size of America’s districts hurts the quality of representation that voters receive.
Representatives by Party
The first, Montana Republican Jeannette Rankin, was elected to the House in 1916, two years after her state gave women the vote. But women only began serving in more substantial numbers in the past few decades. More than two-thirds of the women ever elected to the House (261 of 381, including the incoming members of the 118th Congress) have been elected in 1992 or later. From "What are the requirements to be president?" to "Who's running for president?" to "Is Election Day a federal holiday?" − we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Head to our Just Curious section to see what else we can answer.

Leadership
Of the 435 voting seats in the House, 219 are held by Republicans. The House has 435 members, the number representing each state is determined by population. From "How much does the president make?" to "How many amendments are there?" to "What is an oligarchy?" – we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Head to our Just Curious section to see what else we can answer.
The rise of the speaker's influence began in the 1890s, during the tenure of Republican Thomas Brackett Reed. While the minority leader was the head of the minority party, the majority leader remained subordinate to the speaker. The speakership reached its zenith during the term of Republican Joseph Gurney Cannon, from 1903 to 1911. The speaker's powers included chairmanship of the influential Rules Committee and the ability to appoint members of other House committees. However, these powers were curtailed in the "Revolution of 1910" because of the efforts of Democrats and dissatisfied Republicans who opposed Cannon's heavy-handed tactics. An independent state panel has redrawn the political maps for the California’s congressional districts.
Next, the House tried to expand to just 460 seats instead of 483, which would have caused only two states to lose a seat, but that narrowly failed by four votes on the House floor. This left Congress at an impasse, and over the next few years, reapportionment stalled. “The first presidential veto was used on the apportionment law, so it’s been a hot issue from the very, very beginning,” said Margo Anderson, a professor emerita at University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee who studies the social and political history of the census. In fact, until the House was capped at 435 seats2 by the 1929 Permanent Apportionment Act, each apportionment period was regularly accompanied by clashes over how to best divvy up political power in Congress — including the size of the House.
But given the rancor surrounding reapportionment, the law didn’t come without serious consequences for representation. Specifically, it cut requirements that members be elected in single districts and that those districts be contiguous and compact, serving relatively equal-sized populations. This meant a state that lost seats could now draw wildly disproportionate districts to keep power in more rural parts of the state.
The largest committee of the House is the Committee of the Whole, which, as its name suggests, consists of all members of the House. The Committee meets in the House chamber; it may consider and amend bills, but may not grant them final passage. Generally, the debate procedures of the Committee of the Whole are more flexible than those of the House itself. One advantage of the Committee of the Whole is its ability to include otherwise non-voting members of Congress.
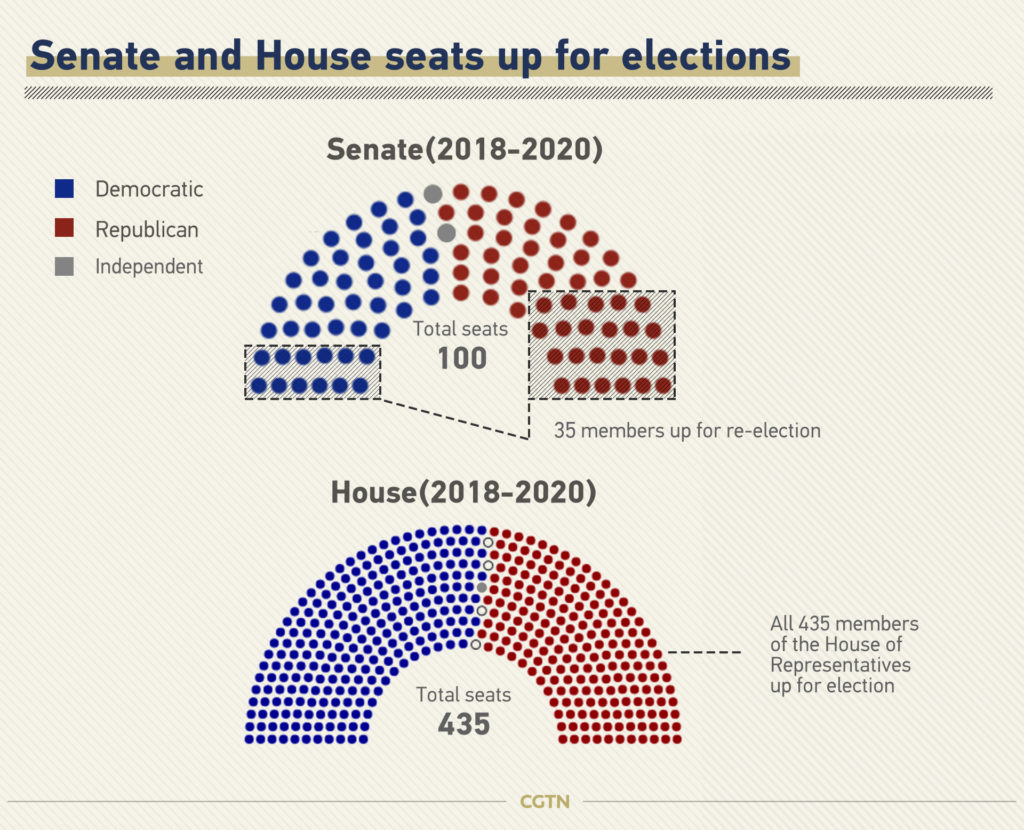
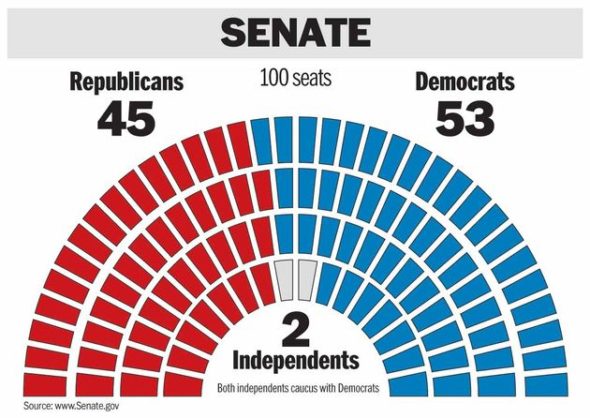
Constitution comes in Article I, Section 2, which guarantees each state, territory or district at least one representative. Prior to the election, the Republican Party had the majority in the U.S. Republicans held 246 seats compared to Democrats' 186 seats, while three seats were vacant. The Republican Party's majority was slightly reduced in 2016, as Democrats picked up six seats. Special elections will be held during the 118th Congress to replace members of Congress who leave office for any reason. The president may veto a bill passed by the House and Senate.